I am a Ph.D. candidate in Computer Science at University of Waterloo & Vector Institute, supervised by Prof. Pascal Poupart. My research interests lie in the intersection of cooperative AI, reinforcement learning (RL), large language models (LLMs), mechanism design, information design and game theory. My recent works mainly focus on mixed-motive cooperation in multi-agent systems, including RL-driven agents and generative agents.
You can reach me at shuhui [dot] zhu [at] uwaterloo [dot] ca.
News
- August 2025: I will be at RLC 2025 Workshop on Coordination and Cooperation in Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning presenting our paper Learning to Negotiate via Voluntary Commitment.
- July 2025: I will be at EC’25 Workshop on Swap Regret and Strategic Learning and Cooperative AI Summer School 2025 presenting our paper Learning to Negotiate via Voluntary Commitment.
- January 2025: Our paper Learning to Negotiate via Voluntary Commitment was accepted to The 28th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics (AISTATS, 2025).
- August 2024: Joined Nomarlity Lab as a research assistant at University of Toronto & Schwartz Reisman Institute, supervised by Prof. Gillian Hadfield.
- July 2024: Attended CIFAR Deep Learning + Reinforcement Learning Summer School.
- January 2022: Started Ph.D. in David R. Cheriton School of Computer Science at University of Waterloo & Vector Institute, supervised by Prof. Pascal Poupart.
- May 2021: Started internship at PerkinElmer as a Machine Learning Engineer.
- September 2020: Started MMath. in Computational Mathematics at University of Waterloo, supervised by Prof. Hans De Sterck and Prof. Jun Liu.
Publications
Talk, Judge, Cooperate: Gossip-Driven Indirect Reciprocity in Self-Interested LLM Agents
Shuhui Zhu, Yue Lin, Shriya Kaistha, Wenhao Li, Baoxiang Wang, Hongyuan Zha, Gillian K Hadfield, Pascal Poupart
Working Paper
Paper | Code
We introduce public gossip as a decentralized reputation mechanism that enables self-interested LLM agents to cooperate in mixed-motive settings. Building on this idea, our ALIGN framework uses hierarchical gossip to assess trustworthiness, sustain reciprocity, and reliably exclude defectors.
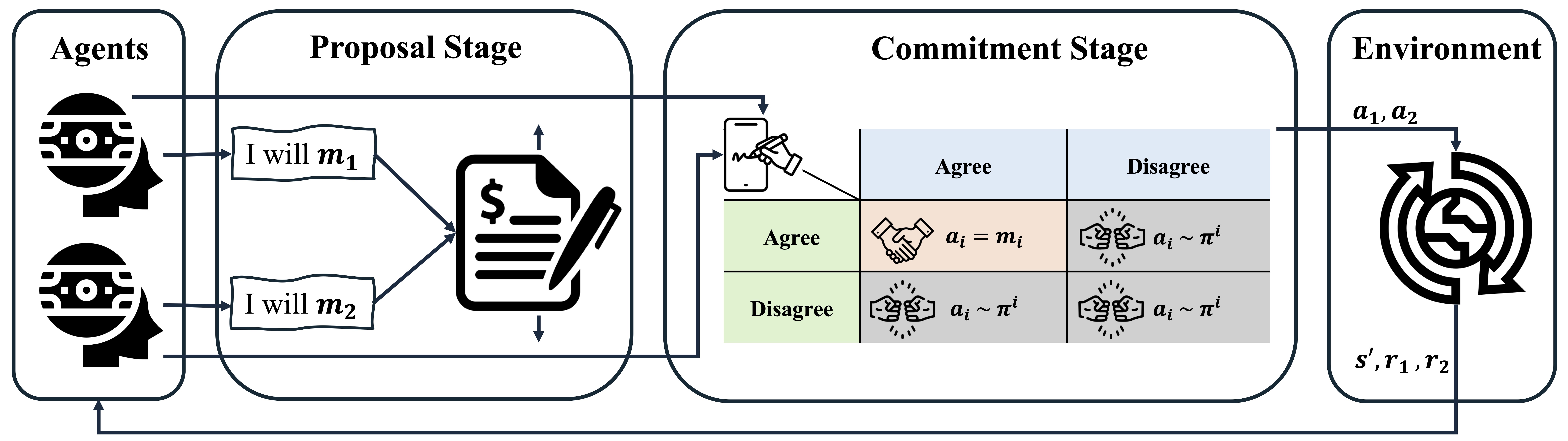
Learning to Negotiate via Voluntary Commitment
Shuhui Zhu, Baoxiang Wang, Sriram Ganapathi Subramanian, Pascal Poupart
AISTATS, 2025
Paper | Code | Talk | Poster
We present a novel framework where agents can voluntarily commit to actions in strategic interactions, improving cooperation in mixed-motive environments.

Policy-Conditioned Policies for Multi-Agent Task Solving
Yue Lin, Shuhui Zhu, Wenhao Li, Ang Li, Dan Qiao, Pascal Poupart, Hongyuan Zha, Baoxiang Wang
Working Paper
Paper
We introduce Policy-Conditioned Policies, a paradigm that represents multi-agent strategies as human-interpretable code and leverages Large Language Models to iteratively synthesize and optimize these programmatic policies for adaptive task solving.
Information Bargaining: Bilateral Commitment in Bayesian Persuasion
Yue Lin, Shuhui Zhu, William A Cunningham, Wenhao Li, Pascal Poupart, Hongyuan Zha, Baoxiang Wang
Working Paper
Paper
This paper reframes Bayesian persuasion as an information bargaining problem to address its complexity in long-term interactions. Unlike one-sided commitment models, the proposed framework enables fairer and more efficient cooperation by balancing the sender's and receiver's roles. Empirical validation using LLMs confirms the framework’s predictions.
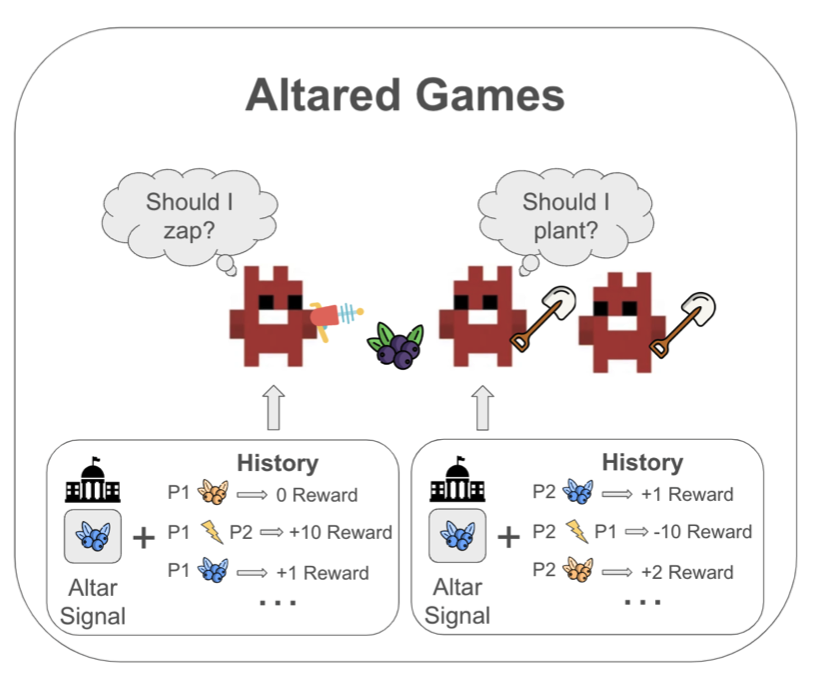
Altared Environments: The Role of Normative Infrastructure in AI Alignment
Rakshit Trivedi, Nikhil Chandak, Andrei Ioan Muresanu, Shuhui Zhu, Atrisha Sarkar, Joel Z Leibo, Dylan Hadfield-Menell, Gillian K Hadfield
Submitted to ICLR, 2024
Paper
We propose Altared Games, a novel Markov game framework integrating a classification institution to enable AI agents to adapt to dynamic norms, demonstrating its effectiveness in enhancing cooperation and social welfare in multi-agent reinforcement learning environments.
Bayesian Persuasion Is a Bargaining Game
Yue Lin, Shuhui Zhu, William A Cunningham, Wenhao Li, Pascal Poupart, Hongyuan Zha, Baoxiang Wang
Submitted to ICLR, 2024
Paper
We reformulate Bayesian persuasion as a bargaining game, demonstrating that the receiver can leverage strategic commitments to counteract the sender’s informational advantage, and validate this perspective through theoretical analysis and empirical experiments with large language models, which exhibit bargaining behaviors in persuasion tasks.
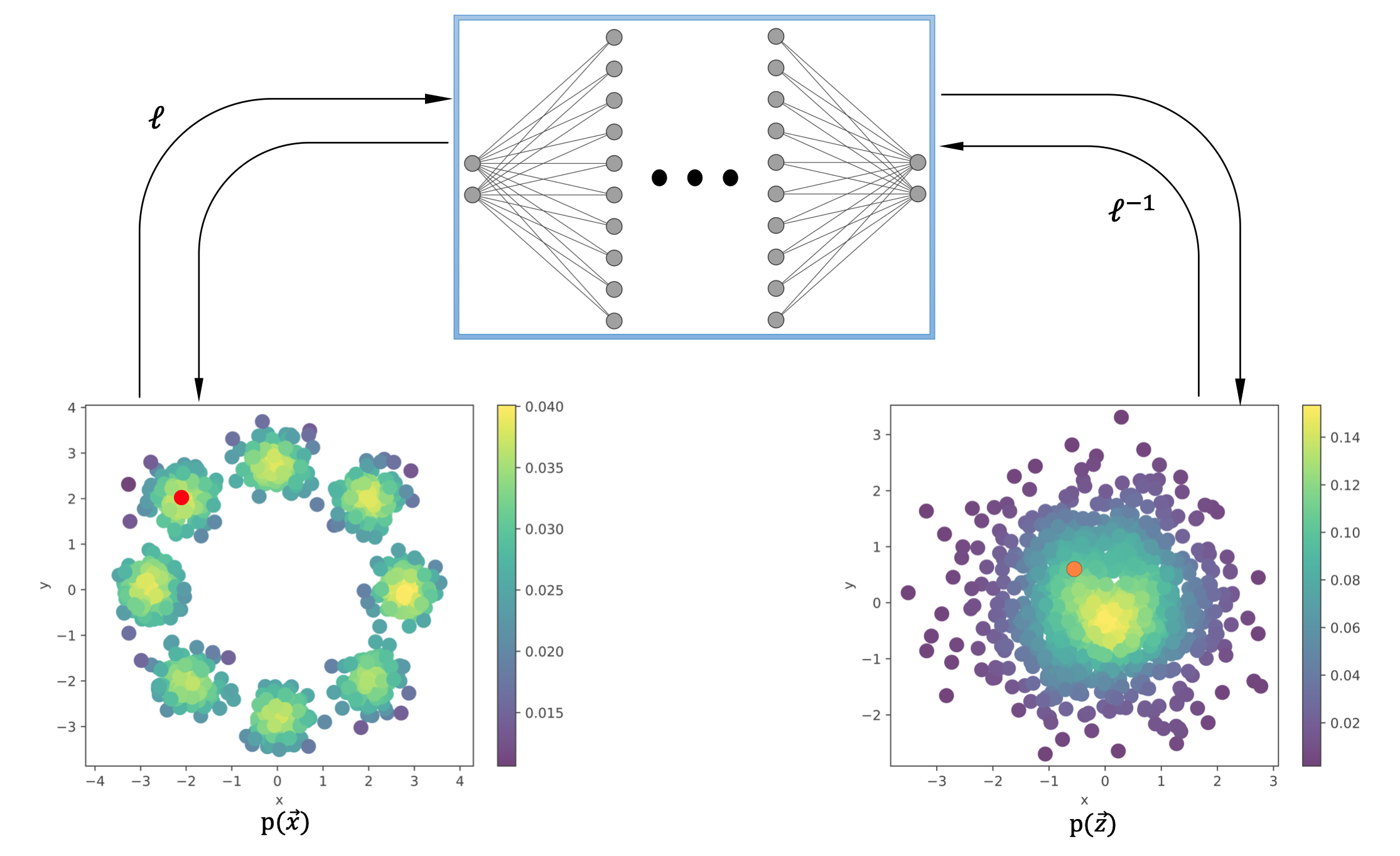
Spline Parameterization for Continuous Normalizing Flows
Shuhui Zhu
Master's Thesis, 2021
Thesis
I develop a Spline-based parameterization method for Continuous Normalizing Flows using Neural ODEs, formulating the problem as an optimal control task to efficiently learn time-dependent patterns while reducing computational cost and maintaining accuracy.
